Buckwheat Nutrition Facts & Health Benefits
Warning: A non-numeric value encountered in /www/wwwroot/www.cookingeggs.net/wp-content/plugins/nutrition-facts-label/nutrition-facts-label.php on line 384
Buckwheat, often called a grain, is actually a seed related to rhubarb. Its culinary use is the same as cereals, their composition of complex carbohydrates.
The nutritional composition of buckwheat
Buckwheat is 72% carbohydrates, including 10% dietary fiber, 3% fat, 13% protein, and 10% water.
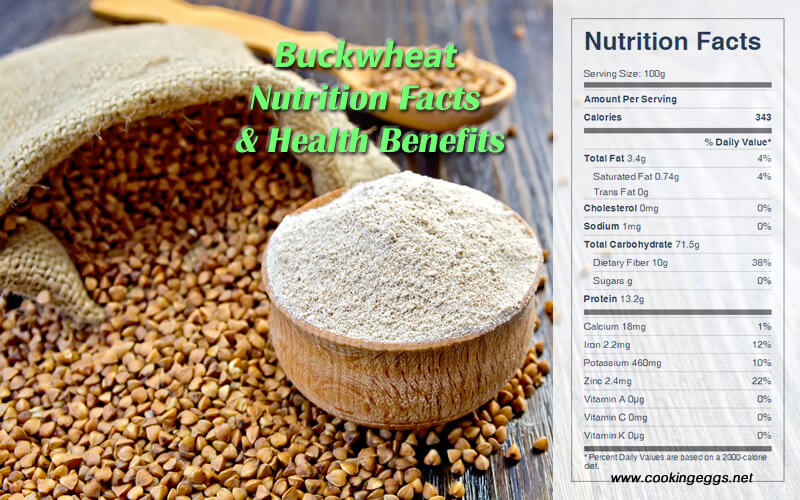
With a 100-gram serving of dry buckwheat providing 343 kcal of food energy, buckwheat is a rich source of protein, dietary fiber, four B vitamins and several dietary minerals, with content especially high in niacin, magnesium, manganese and phosphorus.
One cup of cooked buckwheat groats provides 182 calories, 39.5 g carbohydrate, 6.7 g protein, 1.2 g fat, 5.3 g dietary fiber, 28 mcg folic acid, 174 mg potassium, 8 mg sodium, 139 mg phosphorus, 14 mg calcium, 101 mg magnesium, and 1.21 mg zinc.
Buckwheat Nutrition Facts Label
Health Benefits of Buckwheat
Buckwheat is a pseudograin and not related to wheat at all, with seeds that are similar to sunflower seeds. Buckwheat is commonly used in noodles in Japanese, Korean, and Northern Italian cuisines. It lacks gluten but is high in protein, antioxidants, vitamins B1 and B2, and the minerals iron, zinc, and selenium.
Buckwheat has up to twice the amount of calcium found in other grains. It is rich in vitamins B and E and the amino acid lysine. It also contains rutin, which strengthens the capillaries and is an excellent tonic for the cardiovascular system. Rutin helps people with varicosities and people who bruise easily. Buckwheat has a tradition of use by people wishing to strengthen their kidneys, relieve constipation, and reduce high blood pressure.
Gluten-free: As buckwheat contains no gluten, it may be eaten by people with gluten-related disorders such as celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, or dermatitis herpetiformis. It’s excellent for people with celiac disease because it's protein-rich and gluten-free.
Buckwheat contains diverse phytochemicals, including rutin, tannins, catechin-7-O-glucoside in groats, and fagopyrins, which are located mainly in the cotyledons of the buckwheat plant. It has almost no levels of inorganic arsenic.
Buckwheat is high in a flavonoid called glycoside rutin, which strengthens and tones the walls of the capillaries, the tiniest blood vessels in your body, and so protects against frostbite and chilblains. Buckwheat helps with high blood pressure and atherosclerosis.
Buckwheat contains rutin, a glycoside related to quercetin. Like quercetin, rutin appears to have properties that protect blood vessels, inhibiting platelet aggregation and acting as an antioxidant. It is being investigated for its potential to protect the eyes from diabetic retinopathy, a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness. Rutin helps lower the risk of heart disease as well. One cup of buckwheat provides almost 86 milligrams of magnesium—a mineral that relaxes blood vessels, improving blood flow and nutrient delivery while lowering blood pressure—the perfect combination for a healthy cardiovascular system.
Buckwheat also contains a form of inositol that appears to lower cholesterol and increase insulin sensitivity. This compound is being studied for its potential role in fighting polycystic ovary disease (PCOD) and type 2 diabetes.