Barley Nutrition Facts & Health Benefits
Barley was one of the first grains cultivated by humans. Whole barley contains all eight essential amino acids, making it a complete protein. Here are the nutritional benefits of barley.
In a 100-gram reference serving, cooked barley provides 123 kcal of food energy and is a good source of essential nutrients, including dietary fiber, the B vitamin, niacin, and dietary minerals including iron and manganese.
Raw barley is also a good source of niacin and vitamin B6, as well as the minerals phosphorus, iron, magnesium, and zinc. One cup of barley contains 14.2 percent of the daily value for niacin.Barley also provides some lutein, which may help preserve vision.
Nutritional composition of cooked barley
One cup of cooked, pearled barley provides 193 calories, 44.3 g carbohydrate, 3.5 g protein, 0.7 g fat, 6 g dietary fiber, 11 IU vitamin A, 3.2 mg niacin, 25 mcg folic acid, 146 mg potassium, 5 mg sodium, 85 mg phosphorus, 17 mg calcium, 2.09 mg iron, 35 mg magnesium, and 1.29 mg zinc.
Nutritional composition of raw barley
One-quarter cup of raw, hulled barley provides 163 calories, 33.8 g carbohydrate, 5.7 g protein, 1.1 g fat, 8 g dietary fiber, 10 IU vitamin A, 2.1 mg niacin, 9 mcg folic acid, 208 mg potassium, 6 mg sodium, 121 mg phosphorus, 15 mg calcium, 1.66 mg iron, 61 mg magnesium, and 1.27 mg zinc.
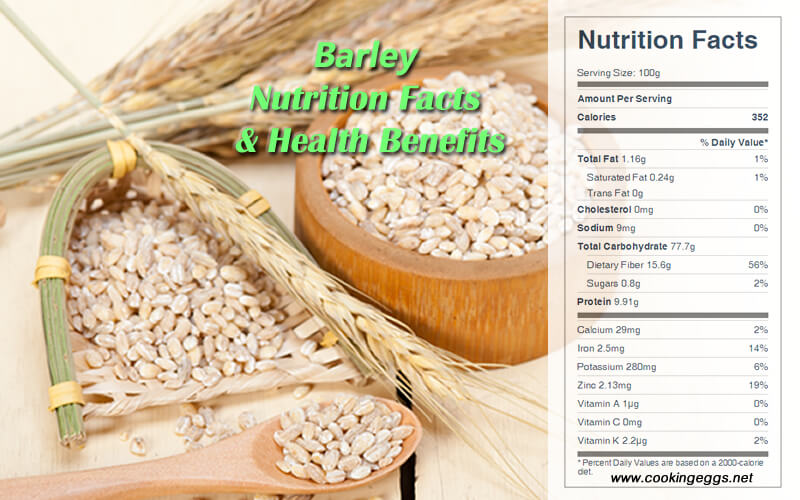
Raw Barley Nutrition Facts Label
Health Benefits of Barley
Barley, which originated in western Asia, is believed to be one of the first grains to be cultivated. It thrives in areas where most other grains refuse to flourish, such as arid or saline soils and even in the arctic climate. It is lower in gluten than wheat is, and is therefore less likely to be allergenic. Barley is esteemed for its high content of protein, carbohydrates, B-complex vitamins, calcium, germanium, iron, phosphorus, potassium, and sulfur. It also contains hordenine, a substance that helps relieve the bronchial spasms associated with asthma.
Barley is considered one of the easiest grains to digest. It can help soothe ulcers and colon or bladder irritations, prevent gallstones, and lubricate dry lungs. It stimulates the liver and lymphatic system, aiding the body in discharging toxins. Barley is good for people who live in cold climates, are frail, or have low self-esteem, because it imparts warmth and vitality to the body.
Barley has been cultivated longer than any other cereal. Bread made from barley was a staple in the Middle Ages. Barley has always been highly valued for its uniquely soothing qualities when used to treat inflammatory conditions of the intestines and urinary tract. Herbalists recommend plenty of barley water to help counter the painful irritation of cystitis and constipation.
Like other grains, barley is mineral-rich, with particularly high levels of calcium and potassium, and plenty of B-complex vitamins. This makes it useful for people suffering from stress or fatigue, and a nourishing food for convalescence. Research on the cholesterol-lowering effects of cereals—wheat, rye, oats, and barley—has found that their coarse outer layers are rich in substances that inhibit the synthesis of cholesterol by the liver.
Barley contains nearly 16% dietary fiber. Fiber helps prevent constipation, and it helps the colon stay healthy by helping intestinal flora produce butyric acid. Dietary fiber also reduces blood cholesterol levels, and whole grain barley contains enough soluble fiber that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recognized it as a food that can reduce the risk of heart disease.
Barley provides magnesium, a mineral that acts as a co-factor for more than 300 enzymes, including enzymes involved in glucose metabolism and the production of insulin. Studies have shown that barley may be even more effective in stabilizing glucose and insulin responses than oats. It appears to regulate blood sugar for up to 10 hours.
Barley's health benefits were observed as long as 2,400 years ago by Indian physicians who recommended substituting barley for white rice, along with losing weight and increasing activity, to treat the disease we now identify as type 2 diabetes.
According to the US Food and Drug Administration, consuming at least 3 grams per day of barley beta-glucan or 0.75 grams per serving of soluble fiber can lower levels of blood cholesterol, a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.
Eating whole-grain barley, as well as other high-fiber grains, improves regulation of blood sugar. Consuming breakfast cereals containing barley over weeks to months also improved cholesterol levels and glucose regulation.
Taken together, barley’s fiber and its B vitamins, which help preserve the health of blood vessels, make barley an especially heart-healthy grain.