Quinoa Nutrition Facts & Health Benefits
Warning: A non-numeric value encountered in /www/wwwroot/www.cookingeggs.net/wp-content/plugins/nutrition-facts-label/nutrition-facts-label.php on line 384
Quinoa is a seed, and the seeds are so tiny that they are eaten whole. It’s usually prepared and used like a whole grain. Quinoa is gluten-free. The seeds are rich in protein, dietary fiber, B vitamins, and dietary minerals in amounts greater than in many grains. Here is quinoa's nutritional value.
Nutritional Composition of Quinoa
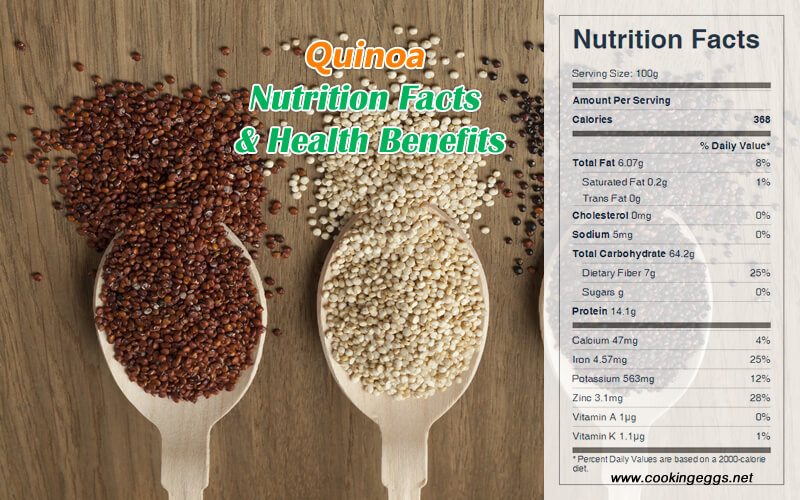
One cup of cooked quinoa provides 222 calories, 39.4 g carbohydrate, 8.1 g protein, 3.6 g fat, 5.2 g dietary fiber, 1 mg sodium, 281 mg phosphorus, 2.76 mg iron, and 0.2 mg riboflavin.
Raw quinoa is 13% water, 64% carbohydrates, 14% protein, and 6% fat. Nutritional evaluations indicate that raw quinoa seeds are a rich source of protein, dietary fiber, several B vitamins, including folate, and the dietary minerals magnesium, phosphorus, and manganese.
After boiling, which is the typical preparation for eating the seeds, quinoa is 72% water, 21% carbohydrates, 4% protein, and 2% fat. In a 100 g serving, cooked quinoa provides 120 kilocalories of food energy and is a rich source of manganese and phosphorus, and a moderate source of dietary fiber, folate, and the dietary minerals iron, zinc, and magnesium.
Quinoa Nutrition Facts Label
Health Benefits of Quinoa
Quinoa is native to the Andes and was a staple food of the Incans. Quinoa is often considered a grain, even though it is not a grass. It is more closely related to beets and spinach. It contains high levels of protein, the amino acid lysine, and calcium. Quinoa is easy to digest and is considered an energy food. A good source of magnesium, manganese, and calcium, quinoa also provides vitamin B2, vitamin E, iron, phosphorus, copper, and zinc. It is higher in fat than many true grains.
Unlike wheat and other grains, it is gluten-free, but it can be substituted for grain in most recipes. Although primarily a carbohydrate, quinoa is relatively high in protein—one cup of cooked quinoa contains about 8 grams of protein—and it contains all of the essential amino acids. It is also a galactagogue, increasing the milk production of nursing mothers.
From a nutrient standpoint, quinoa is a unique plant protein because it contains all nine essential amino acids. It makes for a great plantbased protein source, and it’s also a starchy carbohydrate that’s high in fiber and other phytochemicals. Quinoa is a great gluten-free alternative for anyone with celiac or gluten intolerance.
This tiny seed is also rich in fiber. Fiber is essential for our overall gut health but also induces the synthesis of CYP450 enzymes and protects the liver by reducing the gut bacteria and inflammatory metabolites that would need to be broken down by the liver.
Quinoa also contains bioactive compounds like phenolics that present antioxidant and anticancer properties. Quinoa contains a considerable amount of ferulic, sinapinic, and gallic acids as well as kaempferol and rutin. Combined, these compounds contribute to enhancing immune function and antioxidant benefits for cell repair. It also has antioxidant and anticancer benefits.
All in all, quinoa is a complete protein, and for that alone it is worth adding it to your diet. The fiber in quinoa makes it a great source to boost gut health and improve detox pathways.
Health Risk
Quinoa is a source of oxalates, which may cause problems for those with a history of kidney stones or other conditions that require a low-oxalate diet.
It’s important to wash quinoa very well in cold water before cooking to remove the saponin content. Saponin is a secondary metabolite with anti-nutritional effects. It blocks our absorption of nutrients. The toxicity category rating of the saponins in quinoa treats them as mild eye and respiratory irritants and as low gastrointestinal irritants.
The outside of raw quinoa is covered with saponins, which were traditionally used as a diuretic and laxative. In South America, these saponins have many uses, including as a detergent for clothing and washing, and as a folk medicine antiseptic for skin injuries.