Cauliflower Nutrition Facts & Health Benefits
Cauliflower is one of the cruciferous vegetables. This vegetable is high in fiber and low in calories. According to folklore, cauliflower is said to be beneficial for mental function because it resembles the brain.
Cauliflower is rich in vitamins B6 and C, bioflavonoids, folic acid, biotin, boron, calcium, iron, phosphorus, potassium, and sulfur. It’s a good source of the B vitamins folate, B6, and pantothenic acid. As with most other cruciferous vegetables, it is also a good source of fiber. It also contains anticancer compounds, including indoles and sulforaphane.
The nutritional composition of cauliflower
Raw cauliflower is 92% water, 5% carbohydrates, 2% protein, and contains negligible fat.
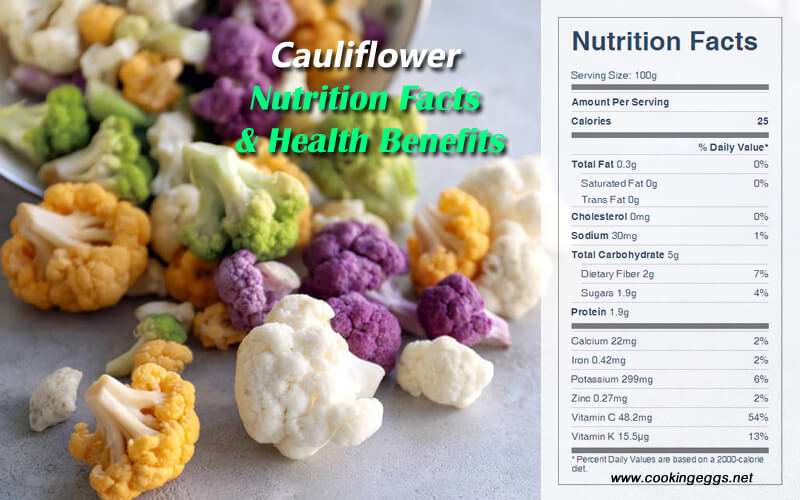
One cup of raw cauliflower pieces provides 26 calories, 5.2 g carbohydrate, 3 g protein, 0.2 g fat, 2.6 g dietary fiber, 20 IU vitamin A, 46 mg vitamin C, 58 mcg folic acid, 304 mg potassium, 30 mg sodium, 44 mg phosphorus, 22 mg calcium, and 16 mg magnesium.
Cauliflower Nutrition Facts Label
Health Benefits of Cauliflower
Cauliflower is a low-calorie, high-fiber, gluten-free alternative to rice and flour. Cauliflower heads can be roasted, grilled, boiled, fried, steamed, pickled, or eaten raw. When cooking, the outer leaves and thick stalks are typically removed, leaving only the floret head. The leaves are also edible but are often discarded.
Cauliflower is one of the vegetables in the species Brassica oleracea. The cauliflower head is composed of a white inflorescence meristem. Cauliflower heads resemble those of broccoli, which differs in having flower buds as the edible portion. Brassica oleracea also includes broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, collard greens, and kale, collectively called "cole" crops, though they are of different cultivar groups.
Cauliflower is one of the cruciferous vegetables that have been shown to help reduce the risk of many types of cancers, including lung, colon, breast, ovarian, and bladder cancers.
Cauliflower is an antioxidant and alterative. It helps move blockages in the body, such as stuck chi, lumps, fibroids, and constipation, and dispels heat in the lungs. Because its anticancer compounds enhance enzyme activity that neutralizes carcinogens so they are unable to attack and transform cells, cauliflower is believed to reduce the risk of colon and stomach cancer in particular. It also aids in the body's metabolism of excess estrogen, helping curb breast cancer and fibrocystic breast disease. Cauliflower has been used to treat acne, asthma, bladder and kidney disorders, constipation, high blood pressure, gout, and obesity. Consumed raw, it helps remedy bleeding gums.
There are four major groups of cauliflower, including white, green, purple, and yellow cultivars.
White: White cauliflower is the most common color of cauliflower, having a contrasting white head surrounded by green leaves. The white cauliflower is unusual among the common crucifers in being relatively low in vitamin A and carotenes, so for someone who is concerned about getting too much vitamin A, cauliflower is a way to get the advantages of some of the brassica diindolylmethane and sulforaphane while limiting vitamin A intake.
Orange: Orange cauliflower contains beta-carotene as the orange pigment, a provitamin A compound.
Green: Broccoflower is another name for green cauliflower.It is available in the normal curd head shape and with a fractal spiral curd called Romanesco broccoli. Green cauliflowers are slightly richer in nutrients than the white ones, with higher amounts of vitamin A and beta-carotene.
Purple: Anthocyanins are abundant in purple cauliflower. The purple color in this cauliflower is caused by the presence of anthocyanins, water-soluble pigments that are found in many other plants and plant-based products, such as red cabbage and red wine.
Cauliflower contains several non-nutrient phytochemicals common in the cabbage family that are under preliminary research for their potential properties, including isothiocyanates and glucosinolates. While boiling reduces the levels of cauliflower glucosinolates, other cooking methods, such as steaming, microwaving, and stir-frying, have no significant effect on glucosinolate levels.