Carambola (Star Fruit) Nutrition Facts & Health Benefits
Carambola, also known as star fruit, is named for its shape: when sliced horizontally, each piece looks like a star, giving it the name of star fruit.
Carambola is a tropical and subtropical fruit native to tropical Southeast Asia. Top producers of carambola in the world market include the United States, Malaysia, Australia, India, Israel, the Philippines, Guyana, and Taiwan. In the United States, carambolas are grown in tropical and semitropical areas, including parts of Florida and Hawaii.
Star fruits are refreshing and have a sweet to sour flavor. The showy fruits have a thin, waxy pericarp, orange-yellow skin, and crisp, yellow flesh with juice when ripe. It usually has five or six prominent longitudinal ridges. In cross section, it resembles a star. The flesh is translucent and light yellow to yellow in color.
There are two main types of carambola: the small sour (or tart) type and the larger sweet type. The sour varieties have a higher oxalic acid content than the sweet types. Some of the sour varieties, like "Golden Star," can become sweet if allowed to ripen.
The entire fruit is edible, including the slightly waxy skin. The flesh is crunchy, firm, and extremely juicy. It does not contain fibers and has a texture similar in consistency to that of grapes. Carambolas are best consumed shortly after they ripen, when they are yellow with a light shade of green or just after all traces of green have disappeared. They will also have brown ridges at the edges and feel firm. Fruits picked while still slightly green will turn yellow in storage at room temperature but will not increase in sugar content. Overripe carambola will be yellow with brown spots and can become blander in taste and soggier in consistency.
Ripe sweet carambolas are sweet without being overwhelming as they rarely have more than 4% sugar content. They have a tart, sour undertone and an oxalic acid odor. The taste is difficult to match, but it has been compared to a mix of apple, pear, grape, and citrus family fruits. Unripe star fruits are firmer, sourer, and taste like green apples.
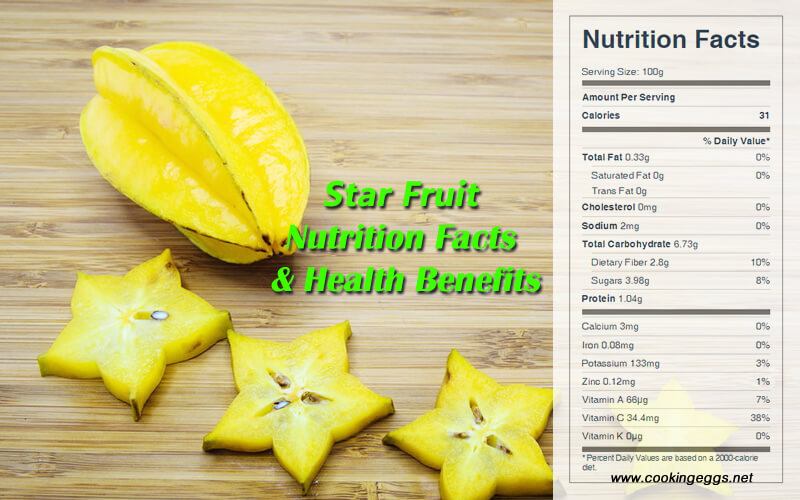
The nutritional value of star fruit
Raw carambola is 91% water, 7% carbohydrates, 1% protein, and has negligible fat. A 100-gram reference amount of raw fruit supplies 31 kcal of food energy and a rich content of vitamin C (41% of the Daily Value), with no other micronutrients of significant content. Star fruit is a good source of betacarotene, vitamin C, and potassium.
Raw Carambola (Star Fruit) Nutrition Facts Label
Health Benefits of Star Fruit
Star fruit is a good source of vitamin C. This is a powerful natural antioxidant. 100 grams of fresh fruit provides 34.4 mg of vitamin C (38% of the Daily Value). In general, consumption of fruits rich in vitamin C helps develop resistance against infectious agents and scavenge harmful, pro-inflammatory free radicals from the body.
Star fruit is rich in anti-oxidant phytonutrient polyphenolic flavonoids. Some of the important flavonoids present are quercetin, epicatechin, and gallic acid. These compounds help protect against the deleterious effects of oxygen-derived free radicals by warding them off the body.
The fruit, along with its waxy peel, provides a good amount of dietary fiber. Fiber helps prevent the absorption of dietary LDL-cholesterol in the gut. The dietary fibers also help protect the mucous membrane of the colon from exposure to toxic substances by binding to cancer-causing chemicals in the colon.
It is a good source of B-complex vitamins such as folates, riboflavin, and pyridoxine. These vitamins help as co-factors for enzymes in metabolism as well as in various synthetic functions inside the body.
Health Risk
Carambolas contain caramboxin and oxalic acid. Both substances are harmful to individuals suffering from kidney failure, kidney stones, or those under kidney dialysis treatment. Consumption by those with kidney failure can produce hiccups, vomiting, nausea, mental confusion, and sometimes death. Caramboxin is a neurotoxin that is structurally similar to phenylalanine and is a glutamatergic agonist.
Like grapefruit, carambola is considered to be a potent inhibitor of seven cytochrome P450 isoforms. These enzymes are significant in the first-pass elimination of many medications, and, thus, the consumption of carambola or its juice in combination with certain prescription medications can significantly increase their effective dosage within the body.