Avocados Nutrition Facts & Health Benefits
Avocados are a super fruit and are very popular in America, They are full of healthy fats and protein, plus antioxidant properties and benefits for our vascular health, here are nutrition facts & health benefits of avocado.
Nutritional Value of Avocados
Raw avocado flesh is 73% water, 15% fat, 9% carbohydrates, and 2% protein. Avocados supplying lots of potassium, also rich in vitamin E, vitamins A, some B and C vitamins, and a little protein and starch, along with avocado oil, which is mainly a monounsaturated fat. One cup of avocado provides 23 percent of the recommended daily value for folate, and avocado is a good source of carotenoids including lutein, zeaxanthin, alpha-carotene, and beta-carotene.
One medium avocado provides 306 calories, 12 g carbohydrate, 3.7 g protein, 30 g fat, 8.5 g dietary fiber, 1059 IU vitamin A, 14 mg vitamin C, 3.3 mg niacin, 113 mcg folic acid, 1097 mg potassium, 21 mg sodium, 73 mg phosphorus, 19 mg calcium, 2.04 mg iron, and 71 mg magnesium.
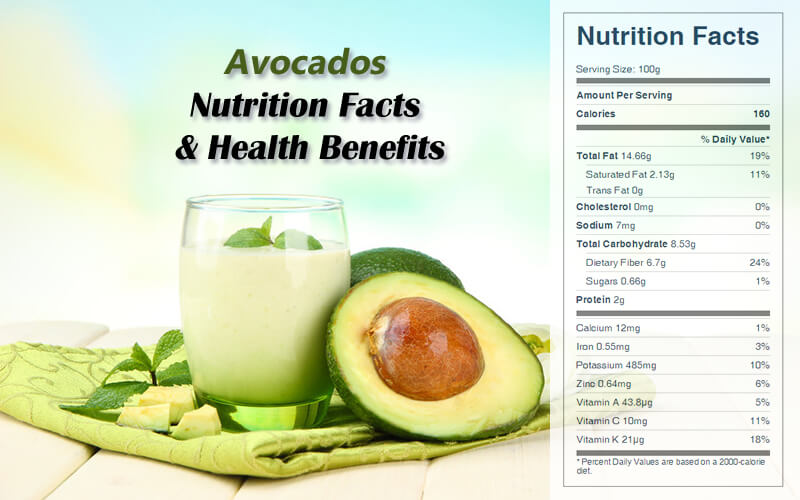
Raw Avocado Nutrition Facts Label
Health Benefits of Avocados
The high nutritional value and concentration of fat, make avocados a commonly used food in vegetarian foods and generally is thought nutritious and healthy. The fruit of avocado has a markedly higher fat content than most other fruit, mostly monounsaturated fat, and as such serves as an important staple in the diet of consumers who have limited access to other fatty foods (high-fat meats and fish, dairy products).
When most people think of an avocado, they immediately think of it as a good source of healthy fats. This is true, but avocado is also extremely high in fiber, it is technically a prebiotic food. They are also rich in protein—the highest amount among any fruits!
The fat contained in avocado is monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA), higher than in any other fruit. MUFAs are a form of anti-inflammatory fatty acids. The fats found in avocados (glycolipids and phospholipids) play a critical role in cellular processes that occur at the cell membrane. Monounsaturated fats have been associated with lowered blood cholesterol. They appear to contain antioxidant compounds that relax blood vessels, which helps lower blood pressure.
Together with heartprotective monounsaturated oil and the other nutrients they contain, they neutralize damaging free radicals. This makes them good for the heart, circulation, and anti-aging.
Avocados contain phenolic compounds of different classes, including (but not limited to) gallic acid, flavonoids, anthocyanidins, and tocopherols. Avocados also have antioxidant properties due to the presence of carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin and alpha- and beta-carotene found in the pulp.
The amount of lutein found in the avocado comprises 70 percent of the total carotenoid content, which is higher than other fruit! They also contain significantly higher amounts of glutathione, an antioxidant that plays a key role in detoxification processes within the body.
Avocados are a good source of potassium, a mineral that helps regulate blood pressure as well as hydration. They are also low in sodium. Therefore, they are included in the health claim authorized by the FDA: diets containing foods that are good sources of potassium and low in sodium may reduce the risk of high blood pressure and stroke.
Avocado gets its color from the presence of xanthophylls, and they bring more than just color. Xanthophylls are known for limiting the damage of blood vessels by reducing the bad cholesterol we know as LDL.
Increasing fiber is imperative for a healthy digestive system, and prebiotic foods—like delicious avocados—are high in fiber that feed the microflora in our gut to keep them flourishing. I guess it’s not a bad idea to have that avocado toast every morning!
Health Tips
An avocado should be slightly soft and a rich dark green, with no dark sunken spots or cracks. You can ripen a less mature fruit at home in a paper bag. Don’t refrigerate them until they are ripe. When you do refrigerate, refrigerate the whole avocado; once they’re cut, they turn brown.
If you must refrigerate a portion of a cut avocado, the flesh is prone to enzymatic browning, quickly turning brown after exposure to air. To prevent this, sprinkle the cut surface with lime or lemon juice and wrap it in plastic.
Generally, avocado is served raw, the flesh of some avocados may be rendered inedible by heat, prolonged cooking induces this chemical reaction in all cultivars.
Avocado allergy
Some people have allergic reactions to avocado, there are two main forms of allergy:
- Those with a tree-pollen allergy develop local symptoms in the mouth and throat shortly after eating avocado;
- Known as latex-fruit syndrome, is related to latex allergy and symptoms include generalised urticaria, abdominal pain, and vomiting and can sometimes be life-threatening.